Is dairy farming cruel? How do cows produce their milk? We answer your questions in this blog.

Dairy products like milk, yoghurt and cheese are common household items, and many people can’t imagine what their meals would look like without them.
When you think about dairy farming, do you imagine an idyllic countryside setting with happy cows spending their lives relaxing in the sunshine? This is far from reality for most dairy cows.
Cows possess many of the same emotional qualities as we do and, like people, some cows are playful, cheeky and outgoing, while others are more sensitive, thoughtful and shy.
All are capable of happiness, though, and cows literally jump for joy when given reason to. But on Britain’s dairy and beef farms, cows suffer both physically and emotionally.
Life in the herd
Cows thrive on social interaction and form close and long-lasting relationships with members of their herd. Semi-wild cattle will groom and graze together, share food and coordinate activities.
For females, the closest and strongest bond they form is with their calf. When about to give birth, the mother will take herself away from the herd for privacy – something that many farmed animals crave but few get to experience.
Later, when she is ready, she will return and formally introduce her newborn to the herd. Her calf will stay with her and suckle for 9-12 months before being weaned.
In captivity, none of this happens.
Life on a dairy farm
Where does milk come from and how do cows produce their milk?
Like all female mammals, cows must be made pregnant to produce milk, which they make specifically to feed their young.
Instead of suckling for a year, the calf is taken away within 24 hours of birth, to stop them from drinking all that valuable milk.
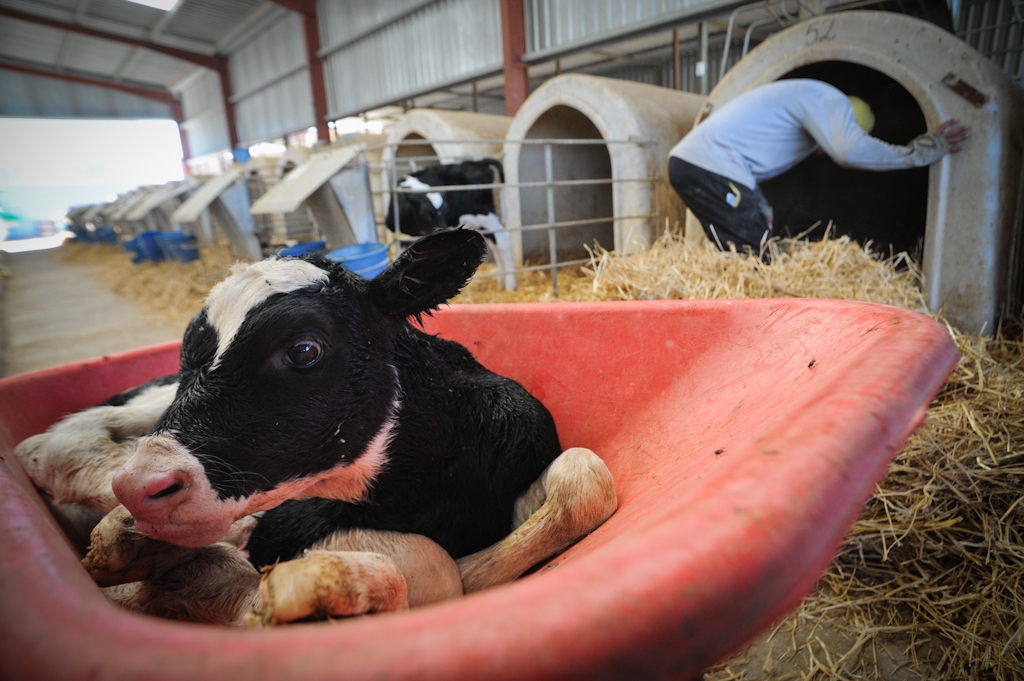

This separation is traumatic for both mother and calf. They will call for one another, sometimes for days, with mothers pacing back and forth, searching for a way to be reunited with their young.
If the calf is female she will one day join the herd and be put through the same cycle of invasive artificial insemination, pregnancy, birth and separation.
If male, his future is less sure.
What Happens to Male Calves?
Male calves cannot grow to produce milk, and often they are not a breed that gains enough muscle to be fattened for slaughter.
So, many are shot at birth and fed to hunting hounds. Others may be reared for low-grade beef, or raised for veal either in the UK or abroad.
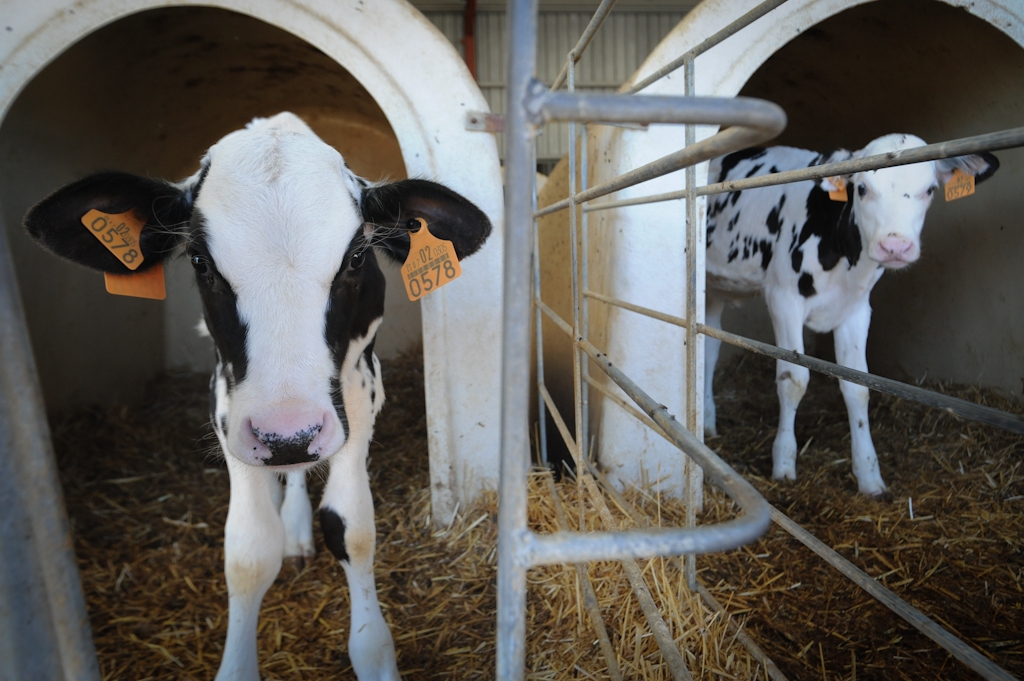

As for the mother, she will be pushed to her biological limits, will lose calf after calf and will be milked until she is worn out, or ‘spent’ as the industry calls it, and her productivity declines.
Then, she will be sent to slaughter. She could have lived 15-20 years but she will be killed at just five or six and her body made into low-grade meat products.
Official records show that even heavily-pregnant cows from the dairy industry are slaughtered in the UK, with their calves left to die on the slaughterhouse floor.
Is Dairy Farming Cruel?
People often think that cows on dairy farms have a lovely life because they have seen some in fields. In reality, they are only turned out to graze for around six months of the year, and the rest of the time they stand around in a barn.
An increasing number of cows are never permitted to go outside at all. They are intensively farmed.
Why waste valuable time getting cows in from fields when you could just keep them in and bring food to them? This is called ‘zero-grazing’ and is exactly what it sounds like. The cows never graze.
Cows used in the dairy industry are bred to produce large quantities of milk – around ten times more than necessary to feed a calf.
The weight of this excess milk distends their udders, causing teat infections and contributing to lameness.
These two conditions, along with infertility, are the main reasons why thousands of dairy cows are sent to slaughter each year at an even younger age than they otherwise would be.
What is Mastitis?
Mastitis is a bacterial infection of the udder that causes painful swelling or hardening. It is frequently attributed to unhygienic, cramped, and poorly ventilated living conditions.
In the UK, in a herd of 100 cows, there could be as many as 70 cases of mastitis every year.
Milk from infected cows has a much higher somatic cell count. When a cow is infected, more than 90 per cent of the somatic cells in her milk are ‘neutrophils’, the inflammatory immune cells that form pus.
With mastitis so prevalent in dairy cows, there is no way to avoid it, and the legal limit for human consumption is 400 million cells per litre.
Lameness
Lameness is commonplace in dairy herds. It is caused by infections such as laminitis and compounded by poor nutrition and long periods standing on hard floors.
It is difficult to comprehend the pain of laminitis but John Webster, Emeritus Professor at the University of Bristol, likened it to us having our fingernails crushed in a door, and then having to stand on those fingertips for hours.
How are Cows Slaughtered?
In the UK, most cows are stunned with a pistol-like captive bolt gun to the brain. Then they are shackled, hoisted and have their throats cut before being disembowelled and skinned.
Whether they are raised for beef or dairy, all cows end up at the slaughterhouse.
Investigations have shown that stunning often fails and cows endure repeated shots to the head or go to the knife while still conscious. The fear they experience is all too clear to see.
This suffering doesn’t need to continue. There are many delicious alternatives widely available in supermarkets, making it easier than ever to go dairy-free.